EXASOL (http://www.exasol.com/en/) provides an in-memory computing solution for data analytics. It combines in memory, columnar storage and massively parallel technologies to support high performance, flexibility and
scalability.
In-memory computing (IMC) is an architecture-style where applications assume all the data required for processing is located in the main memory of their computing environment. In-memory computing (IMC) is a broader concept which includes in-memory database and in-memory analytics. An in-memory database (IMDB, also known as a main memory database or MMDB) is a database whose data is stored in main memory to facilitate faster response times. The source data are loaded into system memory in a compressed, non-relational format. In-memory analytics is an approach to querying data when it resides in a computer’s random access memory (RAM), as opposed to querying data that is stored on physical disks.
What benefits can in-memory computing deliver? The main benefit is it improves the speed dramatically. For example, data processing consists three components: the processor to perform the calculations, the storage to store and manipulate data, and a system to transfer the data between the two. The current bottleneck is the latency storage, more specifically, it is the latency of hard disks. Processing power is not used to full capacity because the data to be processed is not retrieved fast enough from hard disks. Thus, IMC putting data into memory can dramatically speed up
the process of data analysis. The diagram below shows a traditional data warehouse approach vs. IMC-enabled data warehouse approach. The shift from traditional, hard disk-enabled data warehouses to IMC-enabled warehouses implies a reduction in layers on the way from raw data to the results of data analysis.
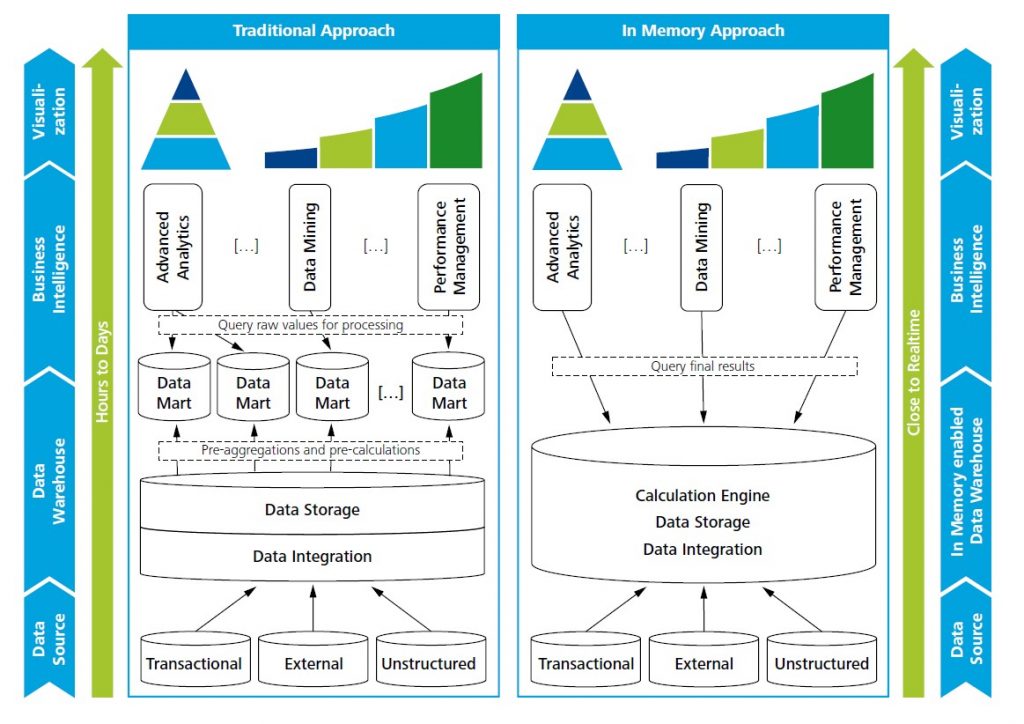
Figure 1. Traditional data warehouse approach vs. IMC-enabled data warehouse approach
Besides the main benefit of quicker speed, IMC can also deliver in process innovation, simplification and flexibility.
- Process innovation: The performance gain of quicker processing speed for data makes it possible to consider the real time data analysis, which could lead the innovative applications.
- Simplification: Due to the reductions in layers on the way from raw data to the results of data analysis, the simpler data models and a more unified interface can be designed.
- Flexibility: Integration of additional data sources and modification of the data analysis is more flexible because the reductions in layers.
In this report, we introduced what in-memory database is and the issues that require attention when considering in-memory computing. We focus our evaluation on the Exasol in-memory database solution in terms of its functionality, deployment solutions and license models. The report aims to give the audience a background understanding of the in-memory database (IMC) and a detail analysis of the Exasol solution.
