By Associate Professor Rebecca Riley and Dr. Abigail Taylor, City-REDI
The BBC has recently highlighted the looming black hole in Local authority Budgets. The average council now faces a £33m ($42m) predicted deficit by 2025-26 – a rise of 60% from £20m two years ago. Unison said the situation meant some councils would not be able to offer the “legal minimum of care” next year. Recent work by City-REDI has highlighted Birmingham City Council as an example of this threat.
Birmingham in Crisis: an example a Local Authority navigating the Black Hole and its Impact.
Recent news has shed light on Birmingham City Council’s financial struggles, triggering a spending freeze and heightened budget scrutiny. Termed “the biggest challenge the council has ever faced” by local councillors, this predicament underscores the pressing issue of local authority budget cuts. While media coverage focuses on failures, it’s crucial to delve deeper into the historical and ongoing equal pay pressures that have burdened Birmingham City Council. Moreover, these challenges are exacerbated by substantial budget cuts that local authorities across the UK have encountered over the past decade.
Understanding Birmingham City Council’s Financial Landscape
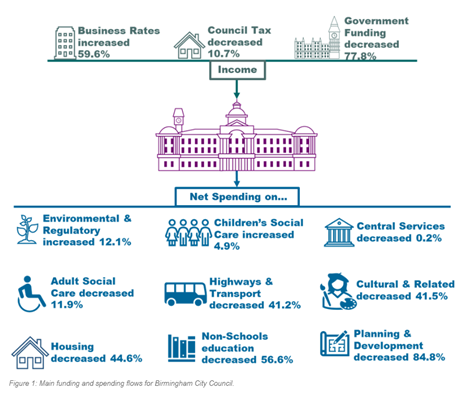
A comprehensive understanding of Birmingham City Council’s financial landscape reveals the sources of its income, changes over time, and expenditure patterns. This analysis, based on the research conducted by City-REDI last year, also delves into the budgetary pressures and their cascading effects on decision-making processes.
The Ripple Effect of Funding Reductions
The impact of budget cuts on UK local authorities cannot be underestimated. Government funding has experienced a drastic reduction due to austerity policies introduced by successive governments. This has led to significant budget slashes, with Birmingham City Council alone enduring austerity cuts amounting to £736 million.
Service Cutbacks: Local authorities rely on funding to provide vital services such as education, social care, waste management, and transportation. When faced with funding reductions, leaders may be compelled to make cutbacks, resulting in diminished service quality or even service cancellations. Birmingham’s Adult Social Care spending decreased by 11.9%, Children’s Services by 4.8%, and environmental protection by 12.1%, as depicted in Figure 1.
Staff Reductions: Budget constraints often force local authorities to reduce their workforce, leading to layoffs, retirements, or hiring freezes. This places additional burdens on existing staff, potentially resulting in burnout. Birmingham City Council’s workforce reduction of 48% (12,000 staff) over a decade jeopardizes its capacity to innovate and develop strategies for efficient financial management.
Infrastructure and Maintenance: Insufficient funding hampers investment in crucial infrastructure development and maintenance. Neglected roads, bridges, and public buildings can pose safety hazards and degrade the overall quality of public assets. Birmingham’s highways and transport budgets have plummeted by 41.2%.
Increased Fees and Charges: To compensate for reduced funding, local authorities may raise fees and charges for services, impacting affordability and straining residents and businesses. However, limited staff and innovation capacity hinder the exploration of alternative income sources, often rendering these efforts less effective.
Capital Project Delays or Cancellations: Funding cuts can lead to delays or cancellations of planned capital projects, hampering economic development, infrastructure improvements, and community well-being. Birmingham’s planning and development budget has suffered an 84.8% reduction.
Economic Impact: Local authorities play a pivotal role in bolstering local economies through initiatives like business support programs and tourism promotion. Funding cuts impede these efforts, potentially hampering job creation, investment attraction, and overall economic growth.
Increased Demand for Social Services: Demographic changes, coupled with funding reductions, strain social services. The pandemic and cost-of-living crisis have exacerbated these challenges, making it difficult for local authorities to meet the growing needs of vulnerable populations.
Navigating Crisis and Building Resilience
Birmingham, as one of Europe’s largest authorities, is grappling with unprecedented budget constraints that have far-reaching implications. Diminished services, strained resources, and challenges in meeting community needs underscore the urgent need for innovative strategies.
In Conclusion
Birmingham City Council’s financial woes highlight the critical issue of local authority budget cuts, compounded by historical and ongoing pressures. As funding reductions cascade across essential services, staff, infrastructure, and economic initiatives, the council faces an uphill battle to maintain quality of life for its residents. Navigating this crisis demands a multifaceted approach, including innovative income generation, strategic resource allocation, and collaboration with the community. Only through these efforts can Birmingham and other local authorities weather the storm of budget cuts and emerge more resilient than before.
- More about Associate Professor Rebecca Riley at the University of Birmingham
- More about Dr. Abigail Taylor at the University of Birmingham
- Back to Business School Blog
The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of the University of Birmingham.
